Case report: monensin poisoning in weaners
Monensin poisoning is believed to have caused the death of 15 weaner calves on a property near Tennant Creek in March. The group of 200 weaners had been processed and yarded 7 days before 15 were found dead with no reported signs of illness prior to sudden death.
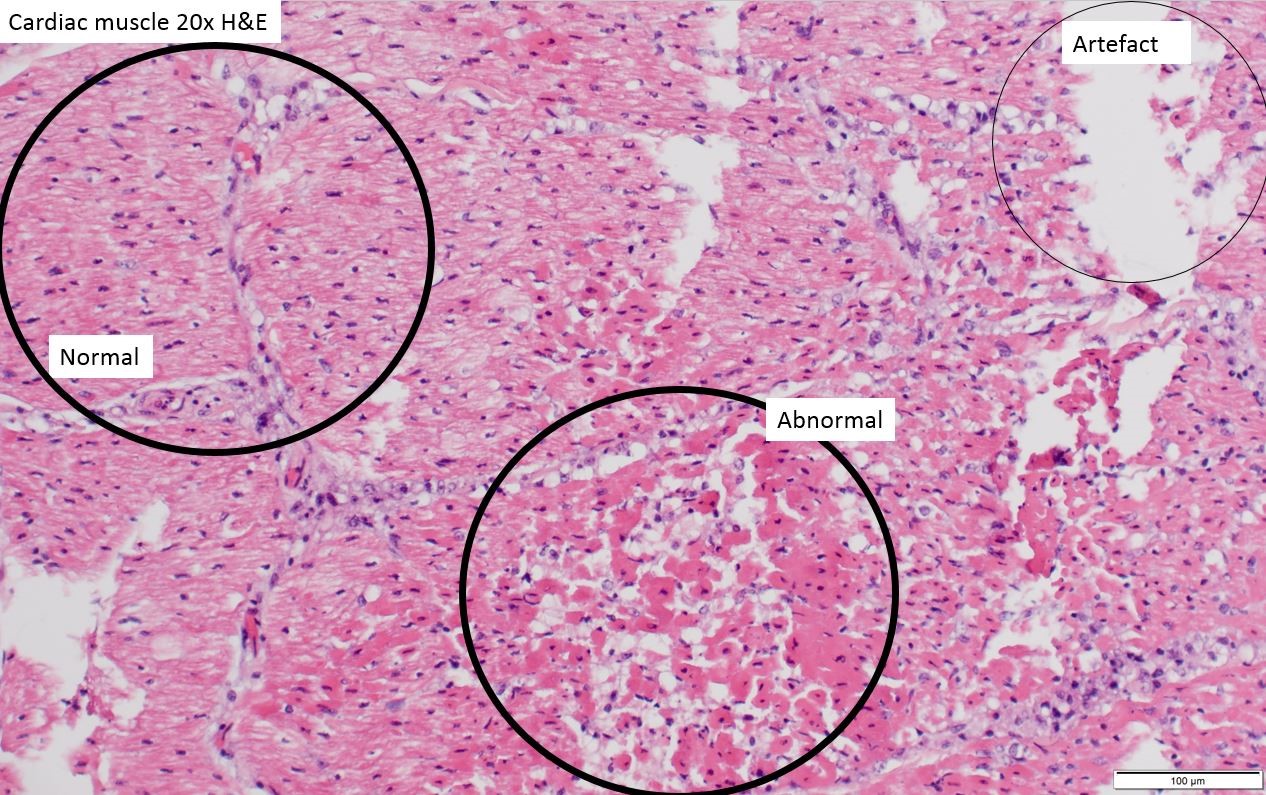
The producer and vet took samples from three of the dead weaners and sent them to the Berrimah Veterinary Laboratories. Lab testing found damage to cardiac tissue (heart) in one of the weaners, which was consistent with exposure to a cardiac poison.
Common sources of cardiac poisons in cattle in the NT include the ironwood tree and ionophore feed additives. Ionophores are a common feed additive used to control coccidiosis and increase growth in cattle and other livestock species. They are safe and effective when administered to the appropriate species at the correct dose, however administration above the recommended dose can be lethal.
There were no ironwood trees present on the property, but the manager reported that a supplement feed containing monensin had been fed to the weaners in the yards. While the feed label said the pelleted supplement contained 50mg/kg monensin sodium, lab testing of a sample of the feed showed it contained a much greater level of 220 mg/kg, which would have been lethal to the weaners taken in a large dose over the course of several days.
Cattle can recover from monensin poisoning, but might later die from sudden heart failure, especially if exercised or they become stressed. There were no clinical signs seen in this weaner group except for sudden death, but affected animals may sometimes have watery diarrhoea, dullness and reduced feed intake.
Deaths can occur for extended periods after exposure to toxic levels of monensin has ceased and there is no treatment. In this case, the feed additive was removed and no further losses were reported.
Figure 13: Microscope image of the damaged heart tissue
To prevent ionophore poisoning in livestock:
- Purchase pre-mixed feed in a pellet form from a reliable source and always read the label
- Use feeds containing ionophores only for the species they were made for, and ensure other species are not able to access these feeds
- Seek professional advice and ensure your dosage calculations are correct if you are adding ionophores to your own feed mix.
For further information see our factsheet on ionophore poisoning.
Give feedback about this page.
Share this page:
URL copied!